Biomarkers, Exposome, and Nutritional & Food Metabolomics Research Group
The research group on Biomarkers, Exposome, and Nutritional and Food Metabolomics belongs to the Department of Nutrition, Food Science, and Gastronomy at the University of Barcelona and is part of the CIBER on Frailty and Healthy Aging (CiberFES) of the Carlos III Health Institute.
Our activity focuses on the investigation of biomarkers of consumption, effect, and disease risk in nutritional, health, and epidemiological studies, using both targeted quantitative metabolomics.
CAPACITIES
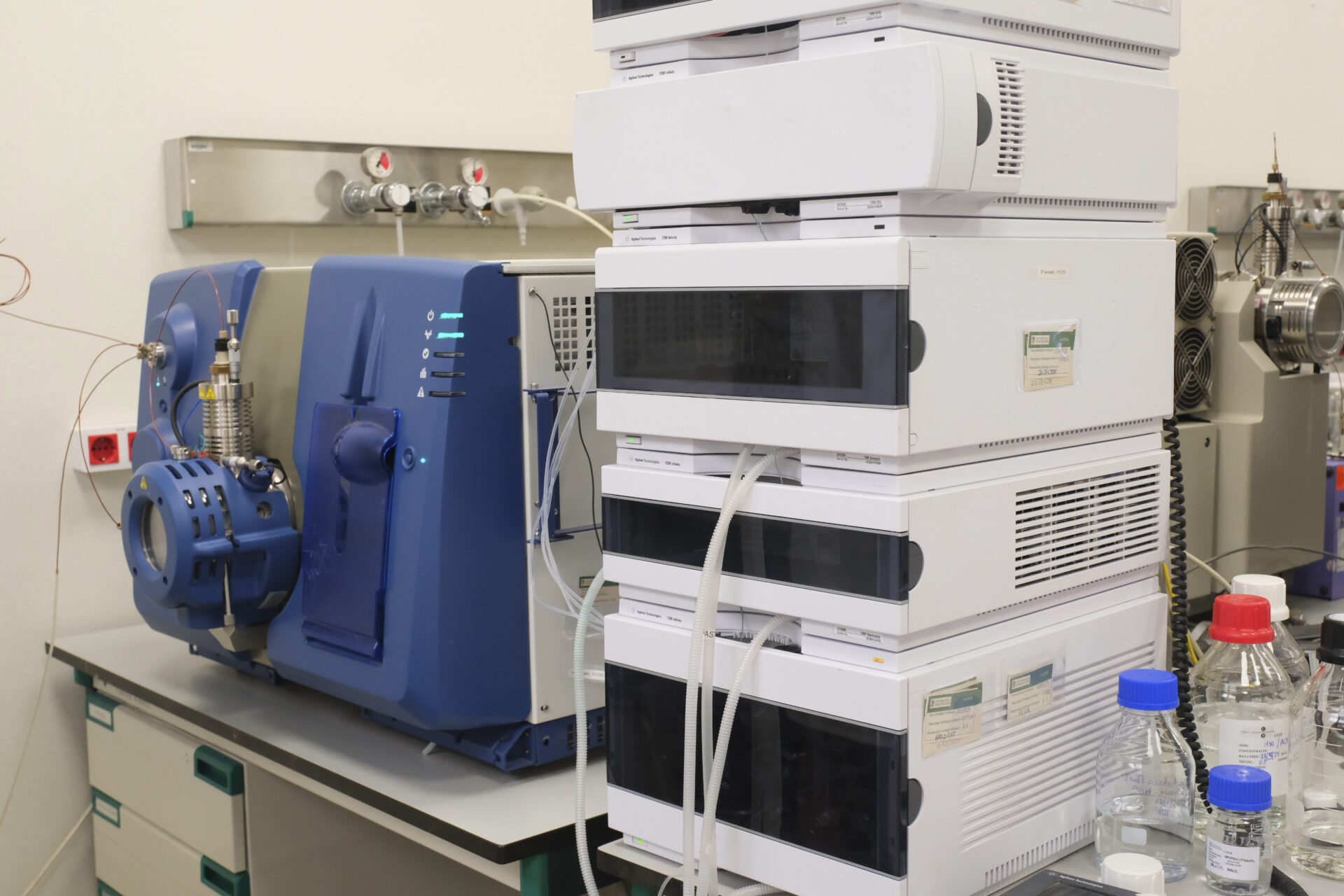
From the University of Barcelona, with the support of the CIBER on Frailty and Healthy Aging (CiberFES) of the Carlos III Health Institute, our research group has developed an innovative methodology for the simultaneous quantification of more than 1,000 metabolites associated with disease risk and prediction.
This technique, with applications in precision medicine and nutrition, allows for rapid results using a minimal volume of biological samples, including serum, feces, urine, plasma, cerebrospinal fluid, and/or saliva.
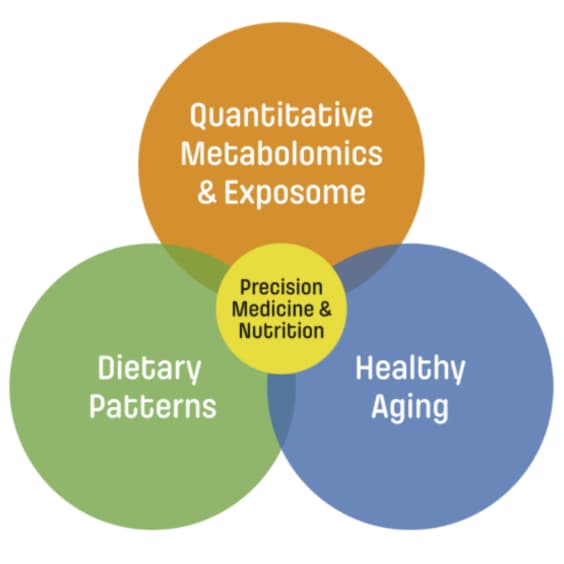
Precision Nutrition and Medicine
The methodology developed by our group enables the investigation of the Exposome through the application of Targeted Metabolomics in various research fields within Nutrition and Precision Medicine.

Food Metabolome

Clinical and Lifestyle Biomarkers

Environmental Pollution Biomarkers
Microbiota Activity

Dietary Assessment

Dietary Recommendations
RESEARCH LINES
-

Study of nutritional biomarkers associated with dietary patterns, polyphenols and bioactive compounds, metabotypes and disease risk phenotypes.
-

Development of food composition tables of bioactive components of interest in nutritional epidemiology.
-

Development of databases of biomarkers of intake and biomarkers of disease risk by metabolomics approach.
-

Standardization of metabolomic analysis protocols in biological samples.
-

Bioinformatics tools for biological interpretation and visualization.
-

Precision and personalized nutrition by studying the effects of dietary patterns and the role of the microbiota-gut-organs axis in healthy aging.
-

Scientific evaluation of food, nutrition, and health messages present in society, and the development of a resource for informed decision-making based on scientific evidence.
Discover the published papers by the group.
News
How can we help you?
Department of Nutrition, Food Science, and Gastronomy
Faculty of Pharmacy and Food Sciences, INSA-UB
University of Barcelona
Diagonal Campus
Avda. Joan XXIII, 27-31, Building B
08028 – Barcelona